In this article we are going to explain the advantages and disadvantages of linked lists used in C++ programming. The linked lists are the best example of an energizing data structure that uses indicators or cursors for its execution. Therefore, knowing the cursor is crucial to knowing how linked lists work. Therefore, if you have skipped the cursor session, we should go back and redo the cursor. We must also be acquainted with dynamic memory share and structures.

Advantages and disadvantages of linked list
Advantages of linked list
- In linked lists there is no need to define an initial size.
- In linked lists the items can be added or removed from the center of the list.
Disadvantage of linked lists
- In the linked list there is no “random” access.
- In linked lists random memory allocation and pointers are required.
- The linked lists have a bigger disbursal over the array.
What is linked lists
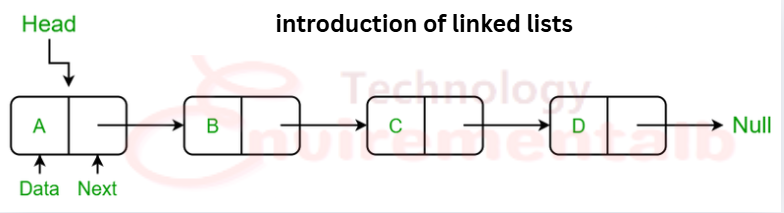
The Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types. In a linked list is a set of random indicated nodes, ordered in such a path that each node consists of one value and one cursor. The cursor ever points to another member of the list. If the cursor is NULL, then it is the last node in the list. The linked list is held using a local cursor variable, which indicatesthe first item of the list. If that cursor is also NULL, then the list is advised (considered) to be empty. Putting the new element in an array of elements is very expensive.
In the above diagram, the linked list is represented by the pointer to the first node of the list. As the head is shown in the diagram, the first node is called the head. If the linked list is empty, as shown in the above diagram, then the linked list is called Null, and each node in the linked list consists of two parts, as shown in the above diagram: one is data, and the second is a pointer.
Types of linked lists
There are different types of linked lists that are as follows:
- Singly linked lists
- Double linked lists
singly linked list
A singly linked list is the way to store a collection of elements. Like an array, these elements can be character (alphabet) or integers. Each element in a linked list is stored in the form of a node.is in the following form.
The one node is a collection of two subparts, as the following upper diagram shows.
The malloc( ) is used to dynamically identify a single piece of memory in C; it is present in the header file stdlib.h.
The sizeof() is used to determine size in bytes(8 bits) of an element in C. Here it is used to determine size of every node and sent as a parameter too.
Doubly linked lists
A doubly linked list is a linked data structure that contains of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes(each node is contain the two blocks). and one data field in between. The beginning and ending nodes’mean previous and next links, respectively, indicates to some kind of terminator/ending point, typically a sentinel node or null, to facilitate traversal of linked list. If there is one sentinel node, then the list is circularly linked via the sentinel node. It can be conceptualized as two singly linked lists formed from the same data items but in opposite sequential orders.