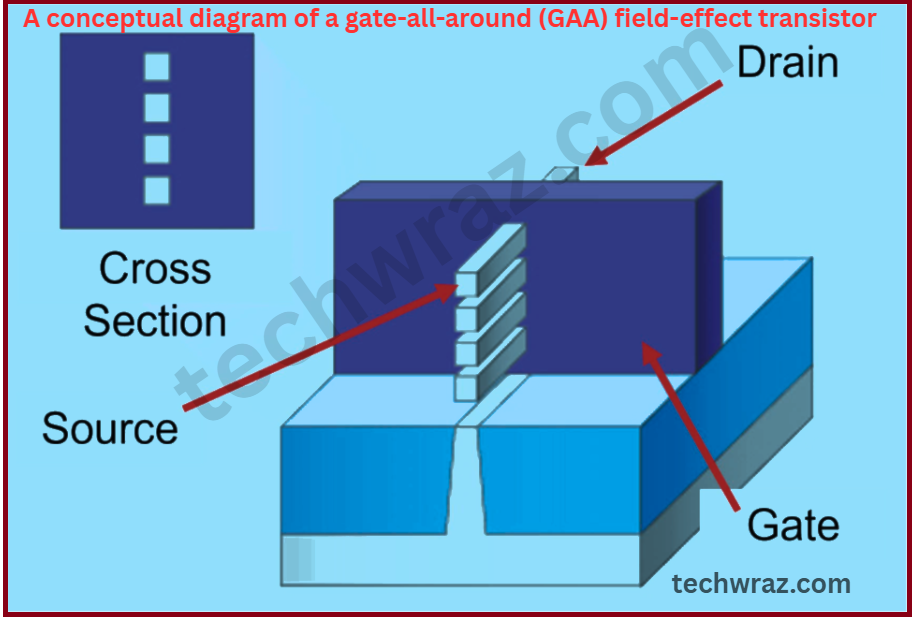
The image shows a conceptual diagram of a gate-all-around (GAA) field-effect transistor. GAA transistors are an advanced version of FinFETs and are designed to operate efficiently at sizes smaller than 7 nanometers. Their 3D structure creates multiple interfaces, which makes the design and analysis process more complex and challenging. This is the latest technology in the field of electronics, particularly in the field of transistors.
A conceptual diagram of a gate-all-around (GAA) field-effect transistor
Pinout detail of gate-all-around (GAA) field-effect transistor
A Gate-All-Around (GAA) transistor does not have traditional “pins” like discrete components (e.g., transistors such as BC547 or 2N2222). Instead, it is a semiconductor structure built inside an integrated circuit. However, we can describe its functional terminals (pins)—similar to a MOSFET—which are:
GAA Transistor Pin Details:
| Pin Name | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Gate (G) | The gate electrode that completely surrounds the channel (hence “gate-all-around”). | Controls the flow of current between source and drain by applying a voltage. |
| Source(s) | The terminal through which carriers (electrons or holes) enter the channel. | Acts as the input terminal for current. |
| Drain (D) | The terminal through which carriers exit the channel. | Acts as the output terminal for current. |
| Substrate (Body) (optional in design) | Sometimes connected internally or to ground depending on design. | Provides mechanical support and may influence threshold voltage. |
Keynote about gate-all-around (GAA) field-effect transistor
- GAA designs can use nanosheets, nanowires, or nanoribbons as channels.
- In GAA FETs, the gate surrounds the channel on all sides, improving control over the current flow and reducing leakage compared to FinFETs.
- Improved Performance:
It offers higher drive current, faster switching speed, and lower power consumption compared to FinFETs.
Applications:
Used in advanced CMOS technologies, high-performance processors, and low-power electronics in upcoming semiconductor generations.