C Programming Identifiers and Keywords
In this tutorial, you will learn about keywords and identifiers in C programming that are part of the syntax. Also, you will learn about identifiers and a proper way to name a variable. Keywords and identifiers in C programming play an important role in coding in C.
C Identifiers
In the C language, identifiers are the names given to variables, constants, functions, and user-defined data. These identifiers are defined against a set of rules.
Example
int marks;
char studentName[30];
Here, marks and studentName are identifiers.
Rules for writing an identifier
- An identifier can only have alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and underscores (_).
- The first character of an identifier can only contain an alphabet (a-z, A-Z ) or an underscore (_).
- Identifiers are also case sensitive in C. For example, name and Name are two different identifiers in C.
- Keywords are not allowed to be used as identifiers.
- No special characters, such as semicolons, periods, whitespaces, slashes, or commas, are permitted to be used in or as identifiers.
C Keywords
Keywords are specific reserved, predefined words in C, each of which has a specific feature associated with it. Almost all of the words that help us use the functionality of the C language are included in the list of keywords. So you can imagine that the list of keywords is not going to be a small one!
Properties of Keywords
- All the keywords in the C programming language are defined as lowercase letters, so they must be used only in lowercase letters.
- Every keyword has a specific meaning; users cannot change that meaning.
- Keywords cannot be used as user-defined names like variables, functions, arrays, pointers, etc.
- Every keyword in the C programming language represents something or specifies some kind of action to be performed by the compiler.
There are a total of 32 keywords in C.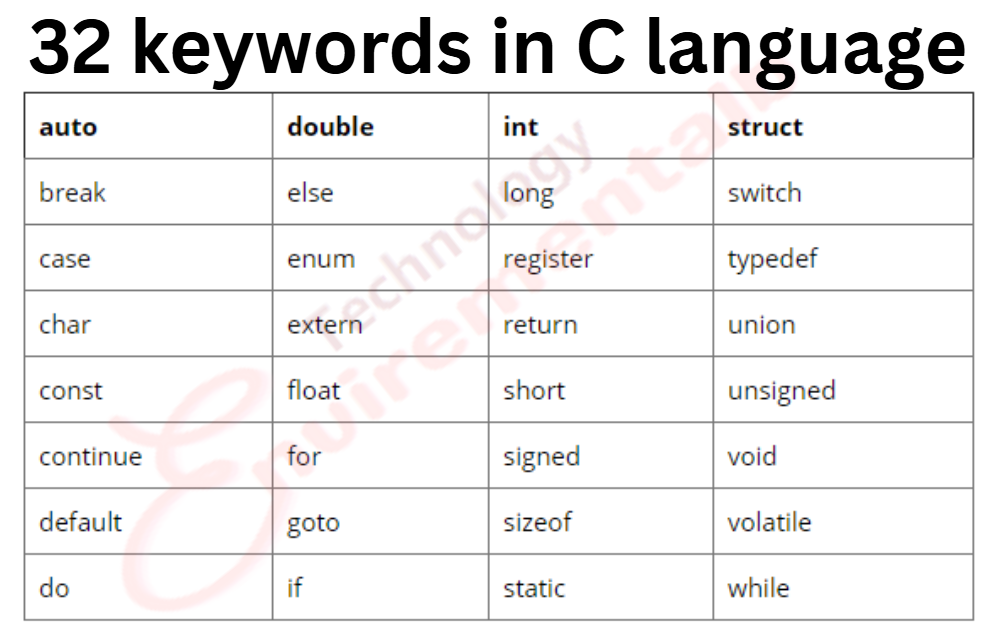
Basics usage of these keywords—
if, else, switch, case, default—Used for decision control programming structure.
break—Used with any loop OR switch case.
int, float, char, double, and long—these are the data types and are used during variable declaration.
for, while, do – types of loop structures in C.
void—One of the return types.
goto—Used for redirecting the flow of execution.
auto, signed, const, extern, register, and unsigned—defines a variable.
return—This keyword is used for returning a value.
continue—It is generally used with for, while, and do-while loops; when the compiler encounters this statement, it performs the next iteration of the loop, skipping the rest of the statements of the current iteration.
enum—Set of constants.
size of—It is used to know the size.
struct, typedef—Both of these keywords are used in structures (grouping of data types in a single record).
union—It is a collection of variables, which shares the same memory location and memory storage