In this article, we have explained the use of transistors as switches in different applications. A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device that can be used for switching applications and amplification of weak signals, and quantities of thousands and millions of transistors are interconnected and embedded into a tiny integrated circuit/chip. A transistor switch is used for ON or OFF of a circuit, so it means that the transistor is commonly used as a switch in electronic devices. Transistors work as a switch when they are in cutoff and saturation regions. In this article, we will explain how to use a transistor as a switch.
Use Transistor As A Switch
Bipolar junction transistors have two junctions: a base-emitter junction and a base-collector junction. Accordingly, there are four different regions of operation in which either of the two junctions is forward biased, reverse biased, or both. But the BJT can be effectively operated in their different modes according to the external bias voltage applied at each junction. i.e., transistor inactive region, saturation, and cutoff. The other region of operation of a BJT is called an inverse active region. The operation of the transistor in these modes is explained below.
The transistor in the cutoff region
In this region, both junctions of the transistor are reverse biased. Hence, the transistor is cut off and does not conduct any currents except for small reverse saturation currents that flow across junctions and can be used as a practical application in PCE San Diego repair shops. In cutoff condition, emitter current is zero, and the collector current consists of small reverse saturation currents. The transistor, when used as a switch, is operated in cutoff-on condition and saturation regions, which correspond to switch-off and switch-on conditions, respectively.
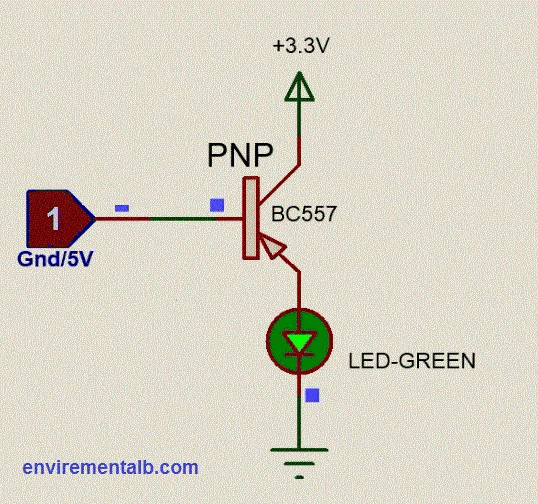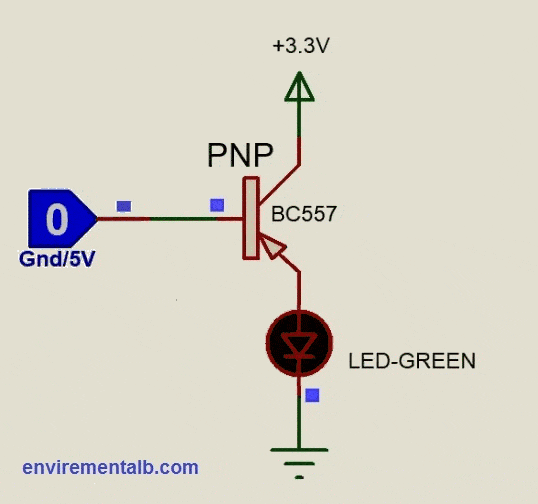
Then we can define the “cut-off region” or “OFF mode” when using a bipolar transistor as a switch as being both junctions reverse biased, IC = 0, and VB < 0.7v. For a PNP transistor, the emitter potential must be negative with respect to the base.
The transistor in the Saturation region
The saturation region is one in which both the emitter-base and base-collector junctions of the transistor are forward biased. In this region, high currents flow through the transistor, as both junctions of the transistor are forward biased and bulk resistance offered is very much less. A transistor in the saturation region is considered to be in the on state in digital logic.
A transistor is said to be in saturation if and only if
β > Ic/I
This is due to the fact that as both junctions of the transistor are forward biased along with electron current flowing from the emitter to the base inactive region, there will be an additional component of electron current flowing from the collector to the base. Small changes in collector-to-base forward voltage lead to large variations in collector currents.
The inverse active region of the transistor
The inverse active region is just inverse or complementary to the active region. In the inverse active region, the base-emitter junction is forward biased, and the base-collector junction will be reverse biased.